# 创建一个JS控制台
作为一个小例子,将创建一个JS控制台。 需要一个输入框,用户可以在其中输入JS表达式,理想情况下应该有一个输出结果的列表。 由于这更像一个桌面应用程序,因此使用了Qt Quick Controls模块。
提示
下一个项目中的JS控制台对测试非常有益。 增强了Quake-Terminal效果,并可以给客户留下深刻印象。 要明智地使用它,需要控制JS控制台的评估范围,例如:当前可见的屏幕、主要的数据模型、单例核心对象或所有这些结合在一起。
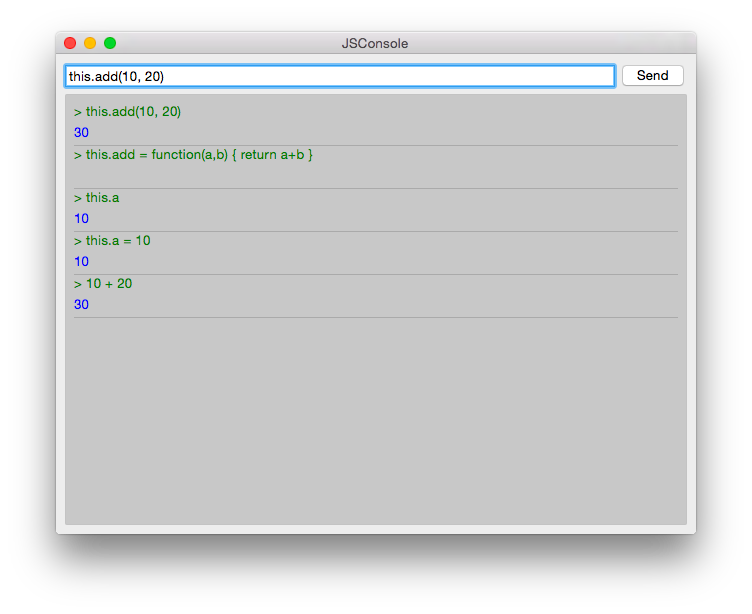
使用Qt Creator创建一个使用Qt Quick控件的Qt Quick UI项目。 将该项目称为JSConsole。 创建向导完成后,已经有了应用程序的基本结构,包括应用程序窗口和退出应用程序的菜单。
对于输入,使用一个TextField和一个Button来发送输入以进行评估。 表达式的求值结果以ListModel为模型、使用ListView显示,两个标签分别显示表达式和求值结果。
应用程序将分割成两个文件:
JSConsole.qml: 应用程序的主视图jsconsole.js: 负责评估用户语句的javascript库
# JSConsole.qml
# 应用程序窗口
// JSConsole.qml
import QtQuick
import QtQuick.Controls
import QtQuick.Layouts
import QtQuick.Window
import "jsconsole.js" as Util
ApplicationWindow {
id: root
title: qsTr("JSConsole")
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
menuBar: MenuBar {
Menu {
title: qsTr("File")
MenuItem {
text: qsTr("Exit")
onTriggered: Qt.quit()
}
}
}# 表单
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 9
RowLayout {
Layout.fillWidth: true
TextField {
id: input
Layout.fillWidth: true
focus: true
onAccepted: {
// call our evaluation function on root
root.jsCall(input.text)
}
}
Button {
text: qsTr("Send")
onClicked: {
// call our evaluation function on root
root.jsCall(input.text)
}
}
}
Item {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
Rectangle {
anchors.fill: parent
color: '#333'
border.color: Qt.darker(color)
opacity: 0.2
radius: 2
}
ScrollView {
id: scrollView
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 9
ListView {
id: resultView
model: ListModel {
id: outputModel
}
delegate: ColumnLayout {
id: delegate
required property var model
width: ListView.view.width
Label {
Layout.fillWidth: true
color: 'green'
text: "> " + delegate.model.expression
}
Label {
Layout.fillWidth: true
color: delegate.model.error === "" ? 'blue' : 'red'
text: delegate.model.error === "" ? "" + delegate.model.result : delegate.model.error
}
Rectangle {
height: 1
Layout.fillWidth: true
color: '#333'
opacity: 0.2
}
}
}
}
}
}# 调用库
评估函数jsCall不单独进行评估,它已被移至JS模块(jsconsole.js)中以进行更清晰的分离。
import "jsconsole.js" as Utilfunction jsCall(exp) {
const data = Util.call(exp)
// insert the result at the beginning of the list
outputModel.insert(0, data)
}提示
为了安全起见,不使用JS中的eval函数,因为这将允许用户修改本地作用域。 使用Function构造函数在运行时创建一个JS函数,并将作用域作为this变量传递给函数。 由于函数每次被创建时候并不充当闭包,也不存储自己的作用域,因此需要使用this.a = 10时将值存储在函数的作用域内。此作用域通过脚本设置成作用域变量。
# jsconsole.js
// jsconsole.js
.pragma library
const scope = {
// our custom scope injected into our function evaluation
}
function call(msg) {
const exp = msg.toString()
console.log(exp)
const data = {
expression : msg,
result: "",
error: ""
}
try {
const fun = new Function('return (' + exp + ')')
data.result = JSON.stringify(fun.call(scope), null, 2)
console.log('scope: ' + JSON.stringify(scope, null, 2), 'result: ' + data.result)
} catch(e) {
console.log(e.toString())
data.error = e.toString()
}
return data
}调用函数返回的数据是一个带有结果、表达式和错误属性的JS对象:data: { expression: "", result: "", error: "" }。 可以直接在ListModel中使用这个JS对象,然后从代理中访问它,例如delegate.model.expression为提供了输入表达式。